Synchronizing Files Between Servers
Occasionally, we may need to synchronize data between servers, such as:
- Synchronizing data between two servers in the same center
- Downloading data from data providers such as WRDS
SSH & SFTP¶
For servers that allow access using SSH, it is currently recommended to use SFTP and the rsync command to perform this task.
rsync is better than other transfer methods?
The rsync -avuz command can automatically compare file modification dates, skipping files that have not been modified, avoiding the waste of time and bandwidth caused by full updates every time. It also automatically compresses, transmits, and decompresses files, significantly increasing the synchronization speed.
As an example, downloading SDC New Issues data from WRDS. The specific process is as follows:
- First, log in to the data source server (
source) using SFTP and determine the path to the data.
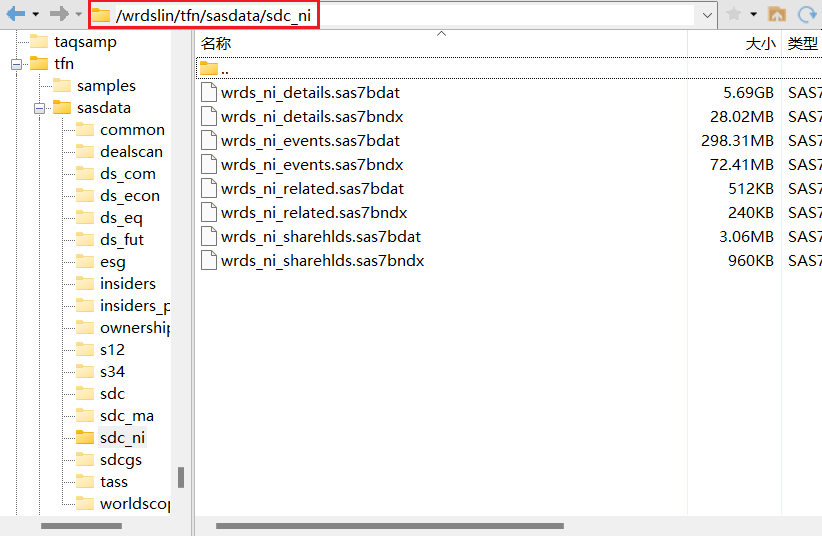
Copy the data path:
-
Set the local path to receive the data, such as
/data/dataset/sdc -
Synchronize using the following command:
Generally, after executing this command, you will be prompted to enter the password. Simply enter the password for the <remote_host> account and press Enter.
The cursor does not move when entering the password
In macOS and Linux systems, the cursor will not move when entering the password. If you see that the cursor is not moving, do not pay attention to it, just enter the password normally and press Enter.
The SSH login port is not the default
rsync -avuz -e "ssh -p 22222" <username>@<remote_host>:/wrdslin/tfn/sasdata/sdc_ni/* /data/dataset/sdc
- You can view the download process through the SSH interface or SFTP.
FTP¶
Some data providers only offer FTP download. In this case, it is recommended to use the lftp command to synchronize.
You can refer to this webpage for basic operations: Linux China
I usually use the mirror <source> <target> method to directly synchronize the entire folder.
AWS S3¶
Some data providers offer AWS S3 service for downloading data. You can refer to the S3 related tutorials for specific operation methods.