PostgreSQL¶
Installing PostgreSQL Server¶
Install PostgreSQL Server according to the official website.
After installation, check if it was successful by running the following command:
It should return the version number of PostgreSQL Server.
Configuring the Server¶
After installation, if you try to access PostgreSQL directly, it will fail.
Error message:
psql: error: connection to server on socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432" failed: FATAL: role "ubuntu" does not exist
To fix this, you need to create a superuser in PostgreSQL for your account. First, switch to the "postgres" user created during the PostgreSQL installation:
Enter the PostgreSQL prompt:
Then, use SQL commands to create a superuser named "ubuntu" with the password "123456" (assuming these values):
To view the list of users:
Exit the PostgreSQL prompt:
Now, when you switch back to your "ubuntu" user, you should be able to open PostgreSQL.
Create a new database named "test":
Enter the "test" database:
To enter the "test" database as the user "ubuntu":
Remote Connection: Server-side Configuration¶
On your local computer, you can remotely connect to the SQL Server on the server using SSL or an SSH tunnel. Here, we recommend using an SSH tunnel.
First, modify the postgresql.conf configuration file of PostgreSQL, usually located at /etc/postgresql/14/main (where 14 is the version number).
Uncomment the listen_addresses parameter and add <local_ip>, which is the IP address of the server:
Next, modify the pg_hba.conf configuration file:
Add a rule to allow your user to access PostgreSQL (the first line is the existing one, and the second line is the new one):
After editing, restart PostgreSQL:
Remote Connection: Local Configuration¶
You can install PgAdmin or HeidiSQL. PgAdmin is a dedicated graphical interface for PostgreSQL Server, while HeidiSQL is a graphical interface for various SQL Servers.
The setup process is similar. Here, we'll use HeidiSQL as an example:
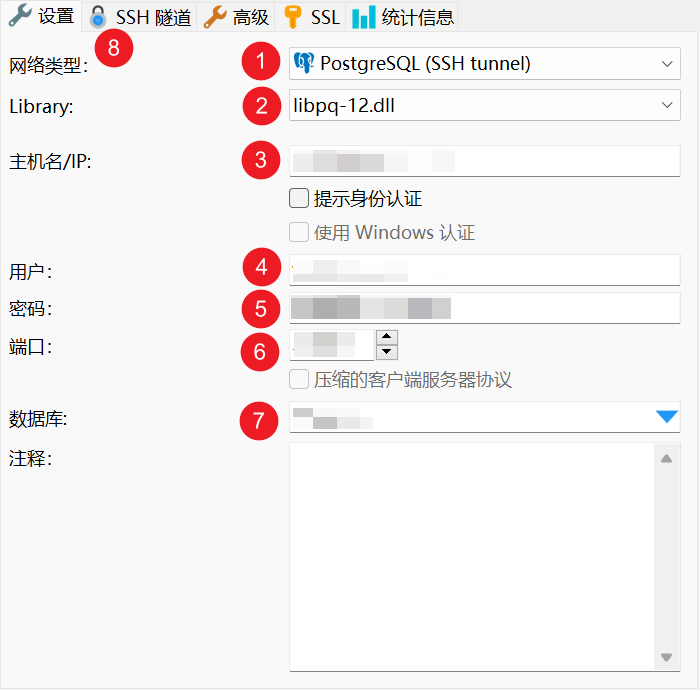
First, enter the SQL-related information, such as the IP address of the PostgreSQL Server, the SQL username and password (not the SSH username and password), and the database name.
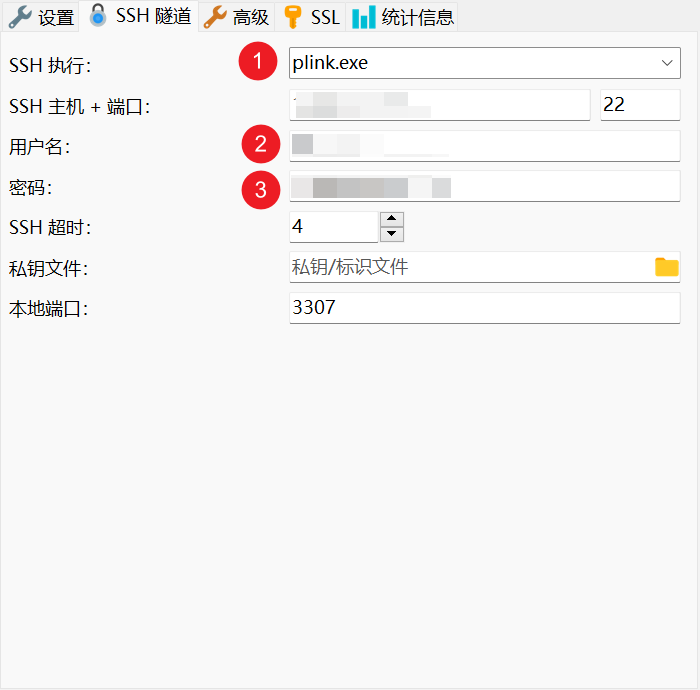
Then, enter the SSH-related information, which is the login information for your server account.
This should allow you to successfully log in. The successful login screen for HeidiSQL looks like this:
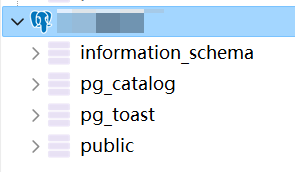
The successful login screen for PgAdmin looks like this: